| The Bettinger research group is involved in organic materials chemistry with a major focus on conjugated carbon
systems ranging from small organic building blocks to carbon
nanotubes. We are particularly interested in synthesizing and studying
boron and boron-nitrogen derivatives of such aromatic systems
for designing materials with particular properties. The boron and
boron-nitrogen reactive intermediates involved in the chemical
manipulations of conjugated carbon systems are studied by
low-temperature spectroscopy (matrix isolation) and by computational
means. In addition, synthetic techniques, conventional
spectroscopy, and modern microscopy techniques are applied in our research. |
|
|
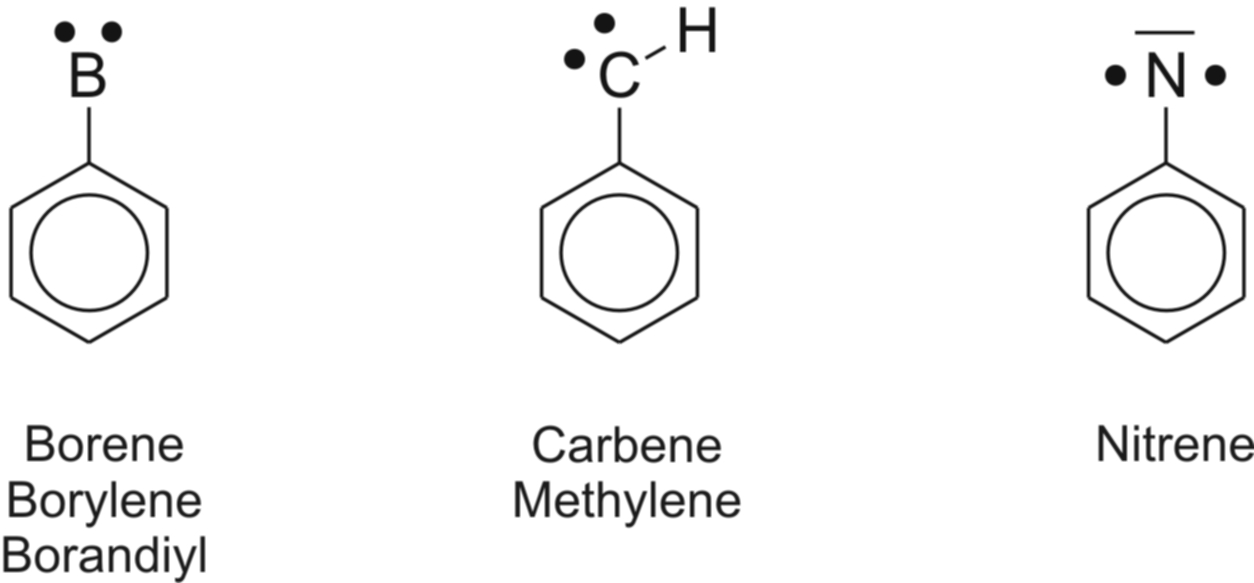
| Subvalent Boron |
Boron compounds receive considerable
interest due to their unusual properties. These generally result
from the tendency of boron to prefer higher coordination numbers than
its position in the periodic table of elements calls for. Lower
coordination as in borlyenes is very rare and unusual, but highly
interesting and possibly also of prepartive interest. Borylenes are the
boron analogs of carbenes and nitrenes, both of which have received
great attention and are used for the synthesis of cyclopropane
derivatives or photoaffinity labeling of biomolecules and materials.
The Bettinger research group is involved in:
- Synthesis, spectroscopic
characterization, and investigation of the chemistry of borylenes under
the conditions of matrix isolation.
- Development of borylenes into synthetically useful reagents for the functionalization of unsaturated carbon systems.
|
|
|
| Boron-Nitrogen Derivatives of Organic Molecules |
The BN unit is isoelectronic to a C2 unit and can thus replace the latter. Well known examples are solid boron nitride and borazine, B3N3H6,
the analogs of graphite and benzene, respectively. But this
analogy can be further extended to reactive intermediates: we are
currently studying borylnitrenes and cyclic
iminoboranes, which are the isoelectronic derivatives of vinylidenes
and arynes, respectively.
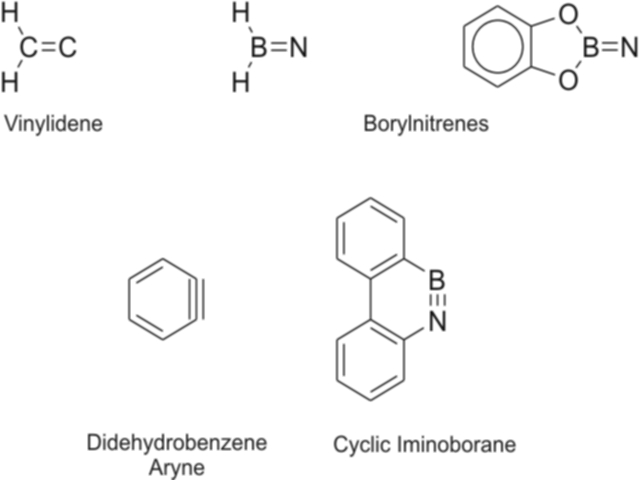
Again,
preparative applications of these reactive intermediates are
envisioned, in particular with respect to the synthesis of BN
derivatives of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
|
|
|
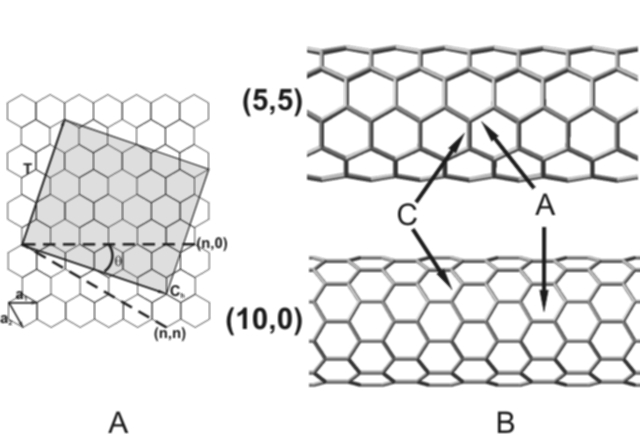
| Carbon Nanotubes |
Research focuses on the chemical
properties of
bare single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNT) with the reactivity towards
subvalent reactive intermediates
being of special interest. The Bettinger research group is performing
fundamental quantum chemical study in order to elucidate the chemical
properties of CNT. We we are also using reactive intermediates for
a targeted modification of CNT.
A rather well investigated functionalized form of carbon
nanotubes is obtained by fluorination. We have previously studied
computationally various aspects of these novel fluorocarbon materials,
e.g., thermochemical stability, hydrogen-bonding properties, as
well as the reactivity. More recently, we have focused on an analysis
of the thermal decomposition products of fluorinated single walled
carbon nanotubes.
|
|
|
|
|
Formation of
carbonaceous materials
|
The formation of hydrocarbon molecules under conditions found in various regions of the interstellar medium, in the
atmospheres of planets, or during terrestrial combustion processes is of broad
general interest. We study protopye reactions by means of computational chemistry
techniques in collaboration with experimental in theoretical groups worldwide.
|
|
|
|
|